
If you are looking for speed, efficiency, and reliability for your computer or application, a solid state drive (SSD) is your best bet. In this comprehensive guide, you are going to learn all about SSDs, from how they work to the benefits of implementing them into your next project.
Let's dive in!
Table of Contents:
- What is an SSD?
- How an SSD Works
- SSD Terms to Know
- The Benefits of Using an SSD
- Different Classes of SSDs
- Types of SSD Interfaces
- What to Consider Before Purchasing an SSD
- Micron SSDs Available at Edge
- Next Steps
What is an SSD?
A solid state drive (SSD) is a storage device used in computers that uses flash memory to store data that is accessed digitally.
An SSD serves as your computer's long-term memory. It stores files even when your device is turned off and works alongside your system's RAM and processor to access and use data, such as your documents, programs, operating system, and even music and games.
Since SSDs have no moving parts to them, they are less prone to failure. Upgrading to one will greatly improve the speed of your computer or application and make it more resilient.
There are a few types of SSDs currently on the market, and we will explore each of them in a later section.
How an SSD Works
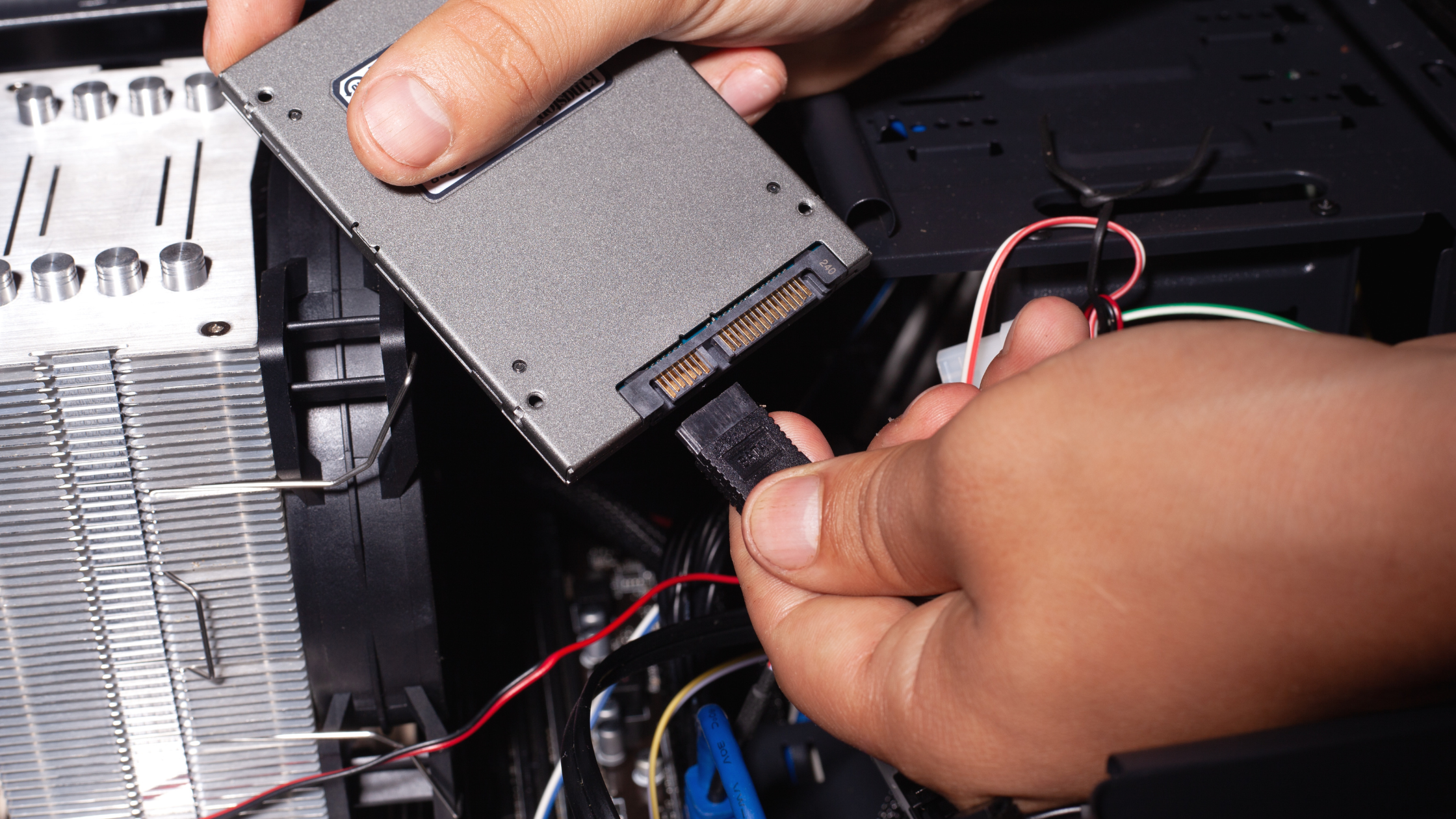
An SSD works by storing data and files in your computer for long-term use, even when the computer loses power or is turned off.
SSDs use a grid of electrical cells to send and receive data quickly. The grids are separated into different sections called pages, where the data is stored. The pages then form blocks.
SSDs cannot overwrite data in individual pages, they can only write data to empty pages in a block. When pages in a block are unused, the SSD will commit the entire block's worth of data to memory, erase the entire block, and then it will re-commit the data from memory back to the block while leaving any unused pages blank.
When a block is erased, the data isn't completely gone, but data can still be securely deleted on an SSD.
However, as expected, your SSD will become slower over time with the more data that is stored on it.
SSD Terms to Know
We've put together a helpful glossary of key terms that you will encounter as you learn more about SSDs.
- Interface - this is where two independent systems communicate. In an SSD, it is a connector that plugs the SSD into the motherboard and power supply. Common SSD interfaces include SATA III and NVMe.
- IOPS (Input/Output Per Second) - a measurement of performance for SSDs and it represents how quickly a given storage device can read and write commands in every second.
- NAND (Negative AND) - the technology that creates flash memory.
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) - a standard hardware interface for SSDs that uses the PCI Express (PCIe) bus.
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell) - contains four bits per cell, allowing for four times the capacity of SLC flash memory.
- Read - accessing a piece of data from memory or a storage drive.
- SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) - an interface that connects a storage drive to a motherboard.
- TLC (Triple-Level Cell) - a type of NAND flash memory that stores three bits of data per cell. Older options of FLASH memory include SLC (single-level cells) and MLC (multi-level cells).
- Wear Leveling - a feature that ensures all NAND cells on a flash-based storage device are used equally to prolong the life of the SSD.
- Work Load - the percent of time that a drive is "read" versus the amount of time the SSD will be "write".
- Write - saving a piece of data to a storage drive.
The Benefits of Using an SSD

There are many benefits to using an SSD in your application. We explore just a few of those benefits in this section.
Efficiency
SSDs rely on less power to operate compared to hard disk drives (HDDs), making them much more energy efficient. SSDs are a much more attractive option for applications such as PCs where battery longevity is important.
Long Product Lifetimes
SSDs have a long product lifetime compared to similar storage devices. In fact, they have an average mean time before failure of 1.5 million hours.
Fast Performance
SSDs can handle data at the super high speeds that are necessary in today's business environment, especially when running programs that need to access large amounts of data.
Smooth and Silent Operation
Since they work with flash technology, the operation of SSDs is smooth and silent, making for a calm and efficient work environment.
Different Classes of SSDs

There are few types of SSD classes, as they are extremely versatile and can be used in many different applications. We will explore a few in this section.
- Client SSDs - SSDs that are associated with client desktop, notebook, tablet, and smartphone applications, and is mostly used for storing operating systems and user data.
- Consumer SSDs - SSDs that are designed to be inexpensive and not intended for use in OEM or IT applications.
- Enterprise/Data Center SSDs - originally developed to replace hard drives, enterprise SSDs are mostly found in enterprise-level data center applications. Many of these data centers that once relied on HDDs now rely on SSDs because they provide a storage solution that will increase performance and efficiency, as well as lower operating costs.
Types of SSD Interfaces
Solid state drives are typically available in a few different interfaces, such as PCIe, SATA, and SAS. Each of these interfaces have evolved greatly over the years.
- PCIe - the fastest and largest interface available on the market today, these drives are equipped with high-performance memory. These drives are ideal for data centers, hosting companies, computing centers, server farms, and more.
- SATA - these drives replaced the previous PATA drives as they are the faster and more efficient memory option.
- SAS - these drives are ideal for high-performance comuting environments with their high throughput and advanced control features.
What to Consider Before Purchasing an SSD
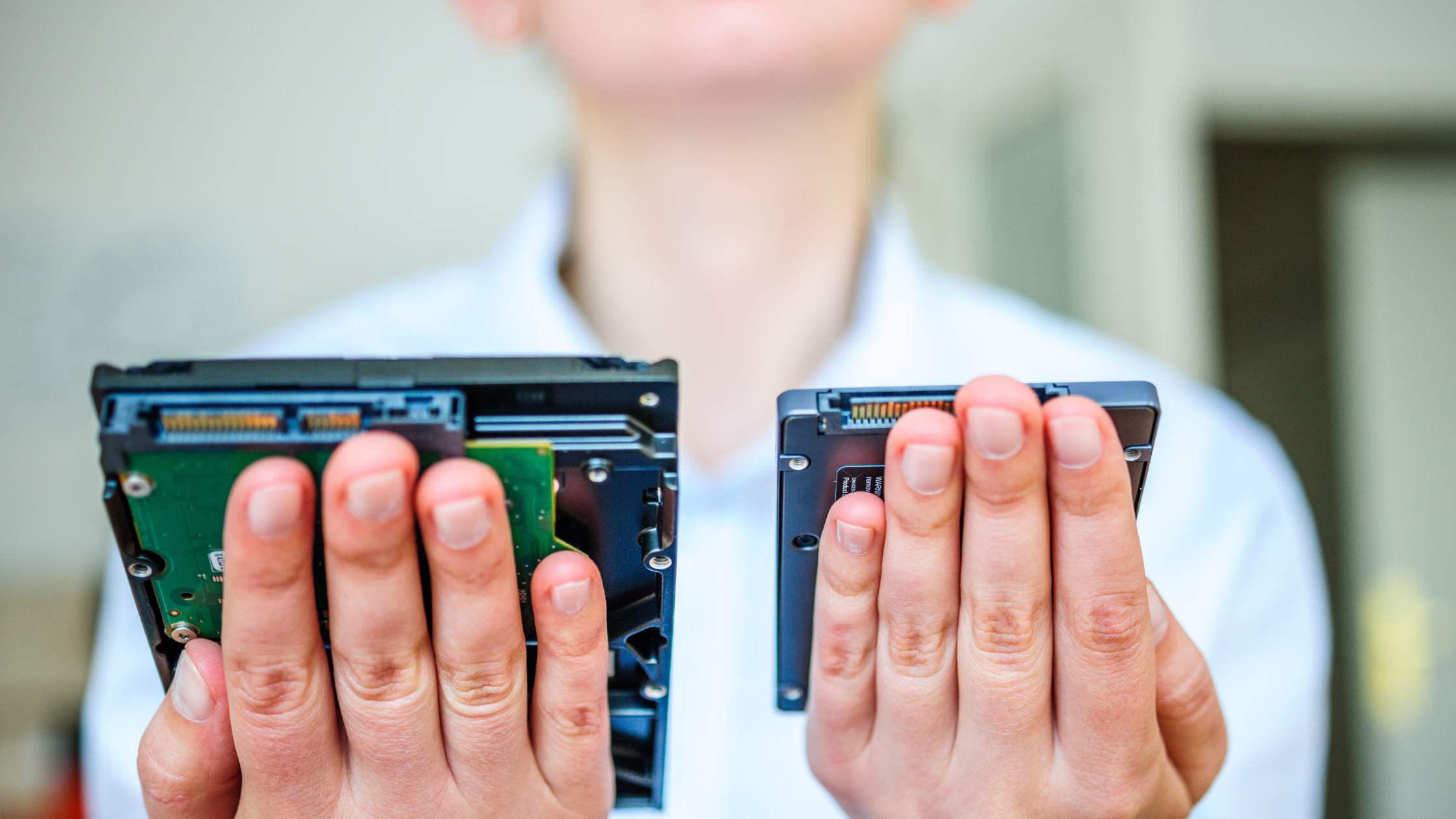

Many factors need to be taken into consideration before selecting and purchasing an SSD for use in your project or application. We explore a few of the key factors in this section.
Speed
SATA drives are typically much slower than NVMe/PCIe drives, since they are serial connection as opposed to the faster parallel PCIe bus.
In fact, NVMe SSDs combined with PCIe connection result in faster rewrite speeds than SATA SSDs.
Endurance
The endurance of an SSD ultimately measures how long the SSD will operate, and it should not be overlooked when purchasing an SSD, especially for larger-scale applications such as data or hosting centers.
Endurance of SSDs vary greatly, and it depends on which type of SSD you end up choosing.
This is where drive writes per day (DWPD) come into play.

For example, let's say your SSD is 128GB and has a warranty time of 5 years. This means that you can write 128GB into the drive every day for the next 5 years.
As mentioned in an early section, SSDs have no moving parts, which it means they don't wear out as easily as an HDD, but unfortunately they don't last forever.
Form Factor
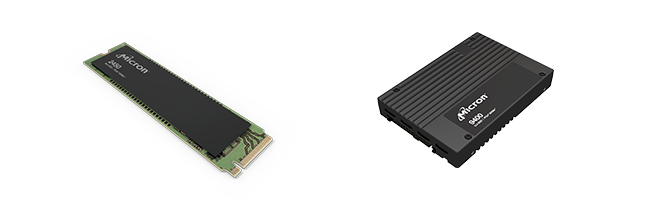
The form factors available for Micron SSDs are M.2 and 2.5-inch (SATA), and U.3 and E1.S (NVMe).
The 2.5-inch form factor is most used as a hard disk replacement for data applications, while the M.2 form factor is used for boot drive in laptops and PCs. The M.2 is tiny and thin, making it the ideal option for small applications.
Security
The security capabilities of your SSD should never be overlooked. While SSDs are typically much more secure than HDDs, it is important that you understand your drive's encryption before purchasing.
Encryption is the process of obscuring data by running it through complex algorithms. A key is required to undo that process and restore the data after its lost.
An SSD that has encryption built into the hardware is called a Self-Encrypting Drive (SED). Micron offers a line of SEDs that support the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) Storage Security Class Opal and Enterprise protocols.
SSDs with hardware encryption offer increased security, maximized system performance, ease of use, and compliance among industry standards and government data security regulations.
Price
Price is a big factor to keep in mind for anyone looking to purchase an SSD for their application, as prices of SSD vary from drive to drive.
Consumer drives are the least expensive, as they consist of the lowest capacities. Client SSDs are the "middle tier" in terms of pricing, as they are used in workplace applications. Lastly, enterprise SSDs are the most expensive because they consist of the best performance and highest endurance.
Micron offers 2 types of drives - PRO and MAX, with the PRO drives being a more economical option and the MAX drives consisting of longer endurance and longer warranties.
Storage Capacity
The capacity of a SSD is determined by the number of NAND chips it has per drive, the number of data cells on each chip, and the number of bits per cell.
Micron SSDs range in capacities from 240GB to 30TB, with the arrival of the new Micron 9400 NVMe SSD.
Here's a brief overview of what each SSD capacity means for your application:
- 256GB-1TB - ideal for boot drive applications.
- 2TB-7.6TB - ideal for storage arrays for large single drive storage.
- 15TB-30TB - ideal for demanding data center workloads and larger capacities.
Power Consumption
Since SSDs consume significantly less power than HDDs, they are ideal for large data center applications.
Micron SSDs Available at Edge

Edge Electronics is an authorized distributor of Micron Technology, an industry-leading manufacturer of solid-state drives and other memory and storage products, such as DRAM Components, DRAM Memory Modules, and NAND Flash.
We offer a wide selection of Micron's comprehensive lines of their high-performing PCIe/NVMe and SATA SSDs.
Read on to learn more about the Micron SSDs we currently stock at Edge:
NVMe:
Micron 2400 Series

The Micron 2400 NVMe SSD is a thin and lightweight SSD that brings industry-leading storage densities to enable flexible OEM solution designs and provides and uncompromising user experience.
It is the world's first and most advanced 176-layer QLC NAND based PCIe Gen4 SSD.
The 2400 series is available in the M.2 form factor (with 3 different sizes) and capacities ranging from 512GB to 2TB.
Benefits:
- Delivers up to two times the performance of previous generation SSDs
- Provides hours of untethered operation for prolonged activity and entertainment
- Enables over 9 hours of battery life
Micron 2450 Series
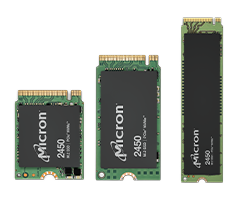
The Micron 2450 NVMe SSD is optimized for next-generation mobile and agile computing, and delivers value and flexibility for anything from entry-level configurations to more demanding applications.
The 2450 series is available in the M.2 form factor (with three different sizes) and capacities that range from 256GB to 2TB.
Benefits:
- Low power consumption
- Engineered for a "worry-free" battery life
- Delivers up to half a million write IOPS
Micron 2550 Series

The Micron 2550 NVMe SSD brings exceptional PCIe Gen4 performance that outperforms the competition and provides an outstanding user experience for daily computing.
The 2550 series is available in the M.2 form factor (with three different sizes) and capacities that range from 256GB to 2TB.
Benefits:
- Sequential read up to 5,000 MB/s and sequential write up to 4,000 MB/s
- 2 million hours MTTF (mean time to failure)
- TCG Opal 2.01 and TCG Pyrite 2.01 security options
Micron 3400 Series

The Micron 3400 NVMe SSD has the capacity to manage workstation, gaming, and corporate PC applications, combining the performance of industry-leading 176-layer NAND and PCIe Gen 4 all while consuming minimal power.
The 3400 series is available in the M.2 form factor (22mm x 80mm) and capacities that range from 512GB to 2TB.
Benefits:
- Built for the most data-intensive applications
- Power efficiency built for all-day computing
- 25% lower idle power than previous generation NVMe SSDs
Micron 6500 ION NVMe

The Micron 6500 ION NVMe is the world's first 200+ layer TLC NAND NVMe SSD that is designed for data centers that need to scale storage affordably.
The 6500 ION series is available in the E1.L and U.3 form factors and the massive 30.72TB capacity.
Benefits:
- Delivers a superior value compared to QLC SSDs
- Lowered operating costs due to low power consumption and better power efficiency
- Reduces data center floor space and carbon footprint
Micron 7400 Series
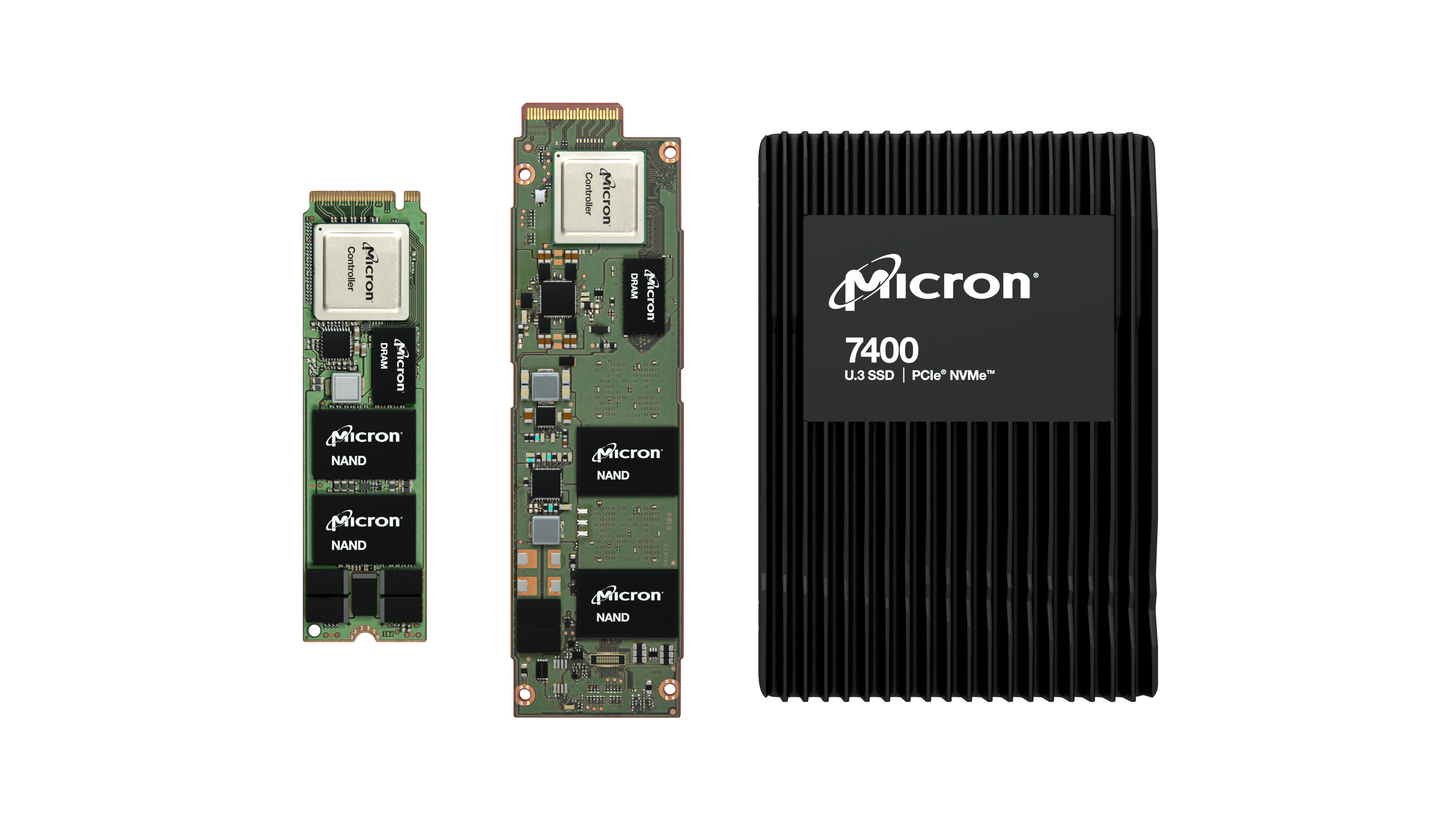
The Micron 7400 NVMe SSD offers an optimal combination of performance, power efficiency, flexibility, and security that will enhance your application. Backed by PCIe Gen4 performance with leading-edge security, the 7400 will meet all your needs in today's fast-paced business environment.
The 7400 series is available in both PRO and MAX models, E1.S, M.2, and U.3 form factors, and capacities that range from 400GB to 3.8TB.
Benefits:
- Combines design flexibility with optimal thermal and cooling
- More than doubles throughput compared to previous generation SSDs
- Backwards compatible to improve performance in PCIe Gen3 servers
This series is going EOL (end of life) at the end of January 2023, meaning they will be obsolete and unavailble for purchase going forward. If you are currently using a 7400 series drive, you can upgrade to the new 7450 series (see below).
Micron 7450 Series
The Micron 7450 NVMe SSD, available in the brand new 176-layer TLC NAND, can optimize your application's boot, cache, and storage needs with its array of form factors, capacities, and deployment options.
The 7450 series is available in both PRO and MAX models, the E1.S, M.2, and U.3 form factors, and capacities that range from 400GB to 15TB.
Benefits:
- Offers the industry's broadest range of PCIe Gen4 SSD form factors
- 2ms and below QoS latency enables impressive responsiveness in data center workloads
- Yields faster read and write speeds, up to 1 million IOPS, enabling faster booting and application responsiveness
Micron 9400 Series

The Micron 9400 NVMe SSD is a high-performance, massive capacity data center solution that sets a new industry standard with a never-before-seen capacity of over 30TB.
The 9400 is available in both PRO and MAX models, the U.3 form factor, the PCIe Gen4 interface, and capacities that range from 6.4TB to 30.72TB.
This series serves as the replacement to the previous generation EOL 9300 NVMe series.
View the Micron 9300 to Micron 9400 NVMe SSD Transition Guide
Benefits:
- Improves power efficiency by up to 77%
- Industry-leading 30TB capacity enables maximum storage density
- Optimized for a wide variety of performance-critical workloads
Micron XTR Series

The Micron XTR NVMe SSD is engineered to provide exceptional durability for write-intensive workloads at cost-conscious data centers.
The XTR is available in the 960GB and 1.92TB capacities and the U.3 (15mm) form factor.
Benefits:
- Enables 10x more endurance than TLC SSDs due to its reliable caching
- Accelerates storage workloads when paired with the Micron 6500 ION
- Meets current security needs with options for TAA compliance and FIPS 140-2 L2
SATA:
Micron 5400 Series

The Micron 5400 SATA SSD is the world's first 176-layer NAND SATA SSD and the most advanced SATA SSD in the industry that is designed to meet your diverse storage needs.
The 5400 series is available in both PRO and MAX models, the M.2 and 2.5-inch form factors, and capacities that range from 240GB to 7.68TB.
This series serves as the replacement to the previous generation 5300 SATA series, which is set to go EOL (end of life) soon.
View the Micron 5300 to 5400 SSD Transition Guide
Benefits:
- Combines Micron's already proven data center SATA architecture with its advanced 176-layer NAND, making for an exceptional user experience
- Offers best-in-class mixed-use performance
- Industry-leading MTTF (mean time to failure) rating that is 50% higher than other leading SATA SSDs
Next Steps

Edge is an authorized distributor of Micron, one of the world's leading manufacturers of memory and storage products. We offer solid support from our very own in-house Micron FAE who can answer all your SSD questions and make recommendations for your specific project.
Our SSD program is comprised of:
- Inventory solutions
- Engineering support
- Specialized Micron FAE on hand to answer all your questions
- Personalized support for your project - we work with you one-on-one to determine the best solutions for your project or application
If you are looking to implement an SSD into your project or application, or upgrade from an HDD, reach out to our specialized Micron FAE, Keith Peterson, and he will provide expert recommendations based on your specific needs.

